The practice of working with robots has been incorporated for some time in many surgical specialties. In cardiac catheterization, great advances in the development of devices have allowed us to treat cardiac conditions that would previously have been unthinkable. The way we perform catheterization has not changed much since 1958, when the first angiography was performed, and physicians are still exposed to disease-causing radiation and have to tolerate the weight of lead aprons. Robots allow us to perform an intervention on a patient, not only from a physical distance, but also a geographical distance. This could be a solution to the problem of certain acute patients accessing – in a timely manner – centers with interventional facilities (24 hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year).
A very advanced system, from Corindus (recently acquired by Siemens) has been around for years, undergoing frequent improvements. Another, lesser-known system is also available – Robocath1.
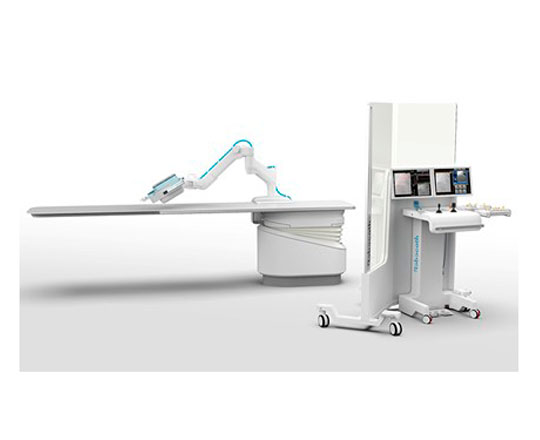
This system has two key components. The first is an articulated arm that holds a device where the guide catheter, angioplasty guidewire, and balloons or stents are placed along with the connections to the infusion pump and saline flush. The second is a mobile control unit, which contains the screens, two joysticks – one to steer the catheter and one for the guidewire – the control for contrast injection and the controls for the table.
The aim of robotic assistance in cardiac catheterization is to perform the procedures safely, comfortably, and accurately, working in the best interests of the patients. It is clear that telemedicine will undergo substantial development in the coming years, as we have seen during 2020 with the COVID-19 pandemic. The problem with robotic assistance in cardiac catheterization is that currently it can be used for simple cases, but a lot of fine tuning is still needed for more complex cases and complications that may arise during procedures. It is a very interesting area of innovation that has a lot of future potential.
BIBLIOGRAFÍA
1. Robocath. 2021. Available at https://www.robocath.com/. Accessed 4 Jan 2021.
Palabras clave: intervención coronaria percutánea, asistencia robótica. Keywords: percutaneous coronary intervention, robotic-assisted.