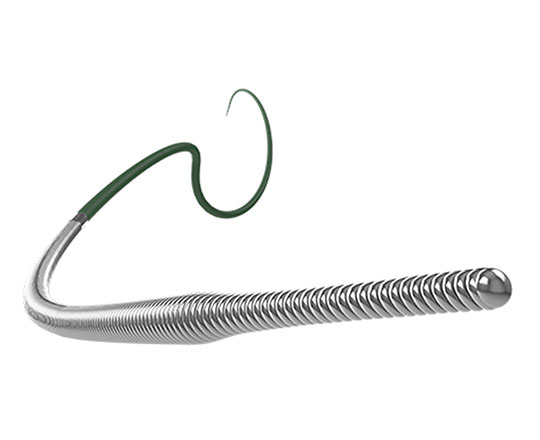
Gaia Next chronic total occlusion guidewire
The Gaia guidewires (Asahi Intecc, Nagoya, Japan), designed specifically for recanalization of chronic total coronary occlusion with precise directional control, have some limitations if the plaque is severely calcified and hardened. In fact, they may even fracture if they are rotated excessively over the plaque without advancing.
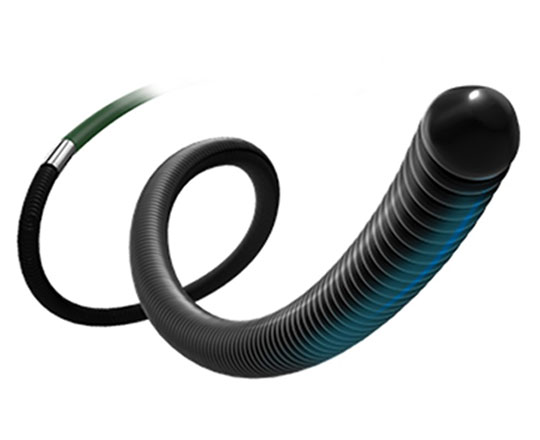
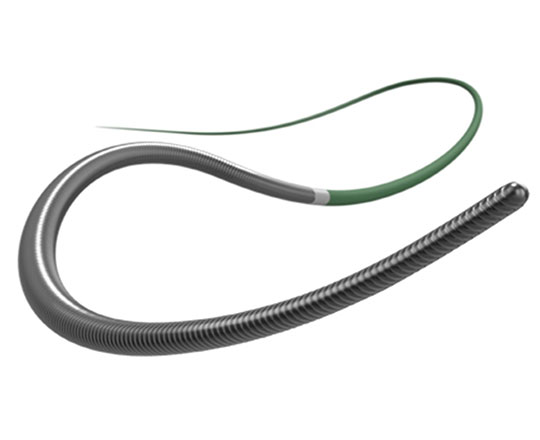
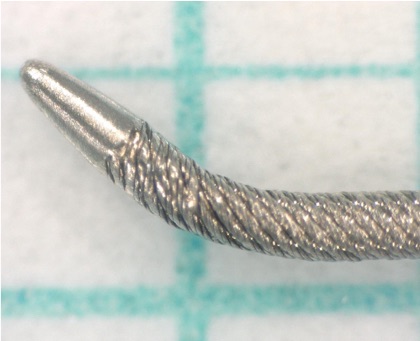
To improve their performance, a family of guidewires named Gaia Next has been developed, though they are not yet available in Europe. They incorporate a technology termed XTRAND coil, in which the main outer coil of the guidewire is made of 7 wires woven together to form a rope, which prevents potential fracture. The XTRAND coil surrounds the guidewire core and the ACT ONE inner coil of the conventional Gaia family. This design means that the wires press against each other when the guidewire is turned in an anticlockwise direction, significantly increasing torque control.
The Gaia Next guidewires have a 40-cm hydrophilic coating at the distal portion which improves lubricity, as it avoids them getting trapped in the plaque, something that occasionally occurs with the conventional Gaia guidewires.
They have a micro-cone tip that is much more tapered and slimmer than the conventional Gaia guidewires, and they are available in 3 sizes: Gaia Next 1, Gaia Next 2 and Gaia Next 3.
| Tapered tip | Tip load (gf) | Penetration force (kg/in2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gaia Next 1 | 0,011 in | 2 | 70,8 |
| Gaia Next 2 | 0,012 in | 4 | 141,5 |
| Gaia Next 3 | 0,012 in | 6 | 212,3 |
I anticipate that these new guidewires will improve the success rate of percutaneous intervention in these complex lesions.
Keywords: Chronic Total Occlusion, coronary wire.