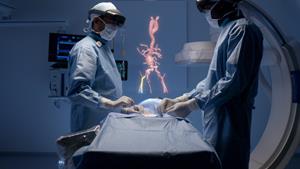
The 2019 Mobile World Congress in Barcelona saw the presentation of an augmented reality system for cardiovascular intervention developed by Philips and Microsoft. The concept of augmented reality is based on the integration of real-time images with live clinical data and 3D medical images to guide procedures accurately and allow the user to concentrate fully on the patient.
This augmented reality system uses images from the new Azurion angiography platform by Philips and a headset with holographic glasses, called HoloLens 2, developed by Microsoft.
Using the HoloLens 2 glasses, Azurion can be controlled in three ways: by voice, eye tracking, or hand gestures. The system allows integration of X-ray and ultrasound images with other 2D and 3D images, meaning that it can be tailored more precisely to the intervention that is to be performed. In reality, HoloLens 2 is a self-contained computer with Wi-Fi connectivity, microphones, spatial audio, electromechanical systems and a power supply.
It is started up with eye movements using Windows Hello and has a holographic visual field that integrates several imaging systems (offline and in real-time) along with 3D clinical data and the controls of the Azurion platform. It safely incorporates Microsoft cloud and artificial intelligence services.
Currently-used systems have large screens showing live 2D images along with other sources of vital data. With this new system it will be possible to work in a 3D augmented reality environment with which doctors will have easy, intuitive and ergonomic control of all available data.
Keywords: Angiography, 3-dimensional imaging, 3D, innovation.