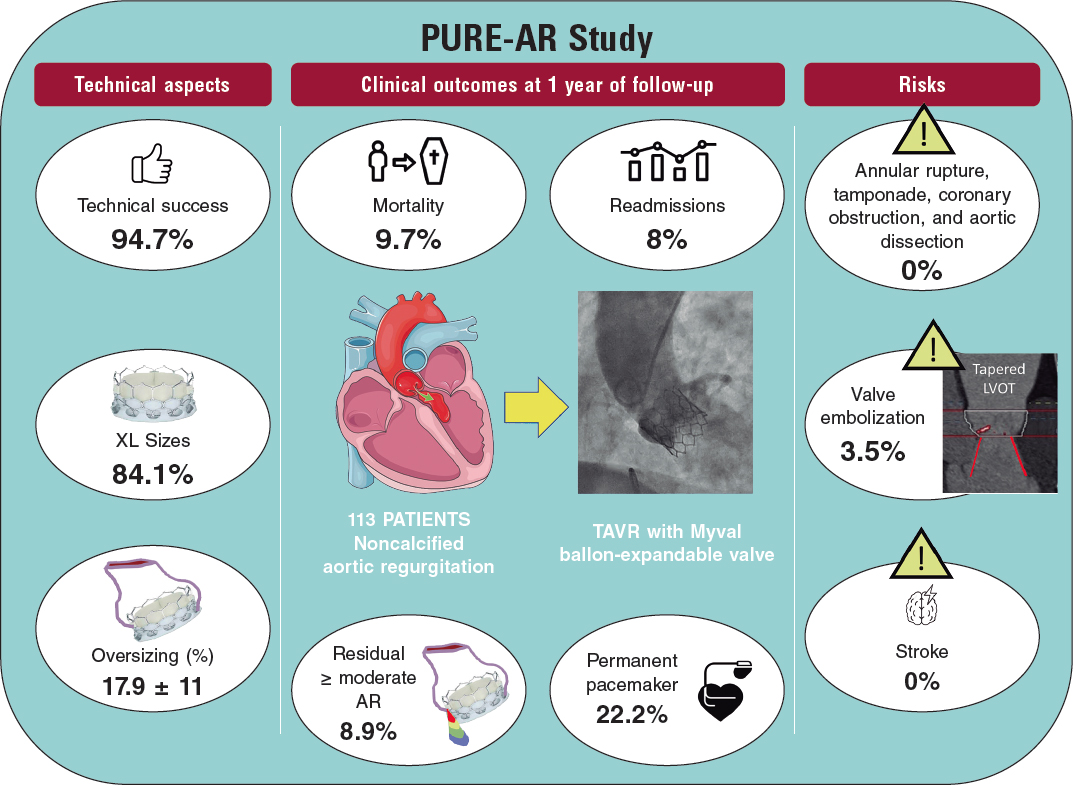
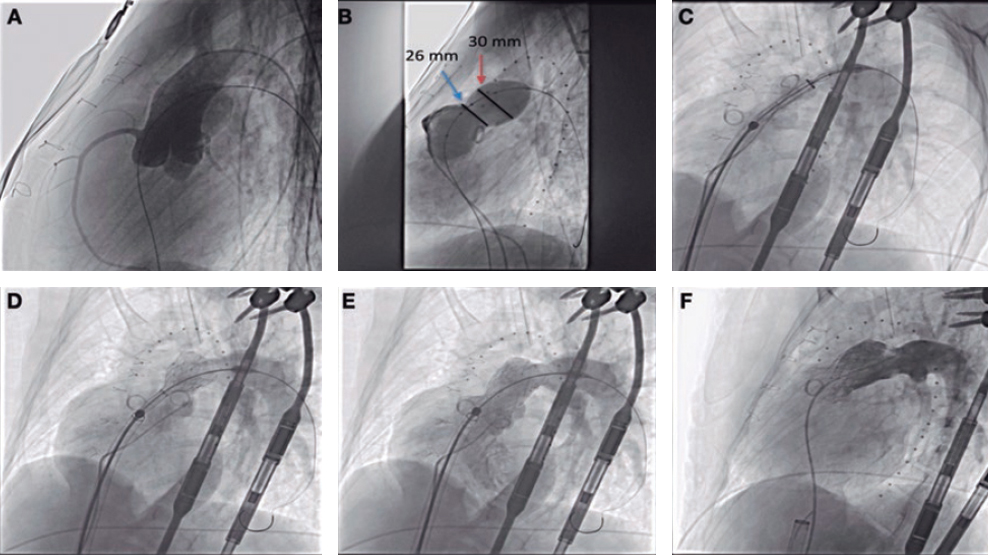
A 75-year-old female underwent aortic valve replacement with a sutureless Perceval valve due to degeneration of the Mitroflow aortic bioprosthesis. She was admitted 2 years later for heart failure. The transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) performed showed a class III-paravalvular leak (PVL) of the left coronary cusp probably due to calcification (figure 1A,B, video 1 and, video 2 of the supplementary data). Our heart team decided to perform percutaneous closure of the PVL.
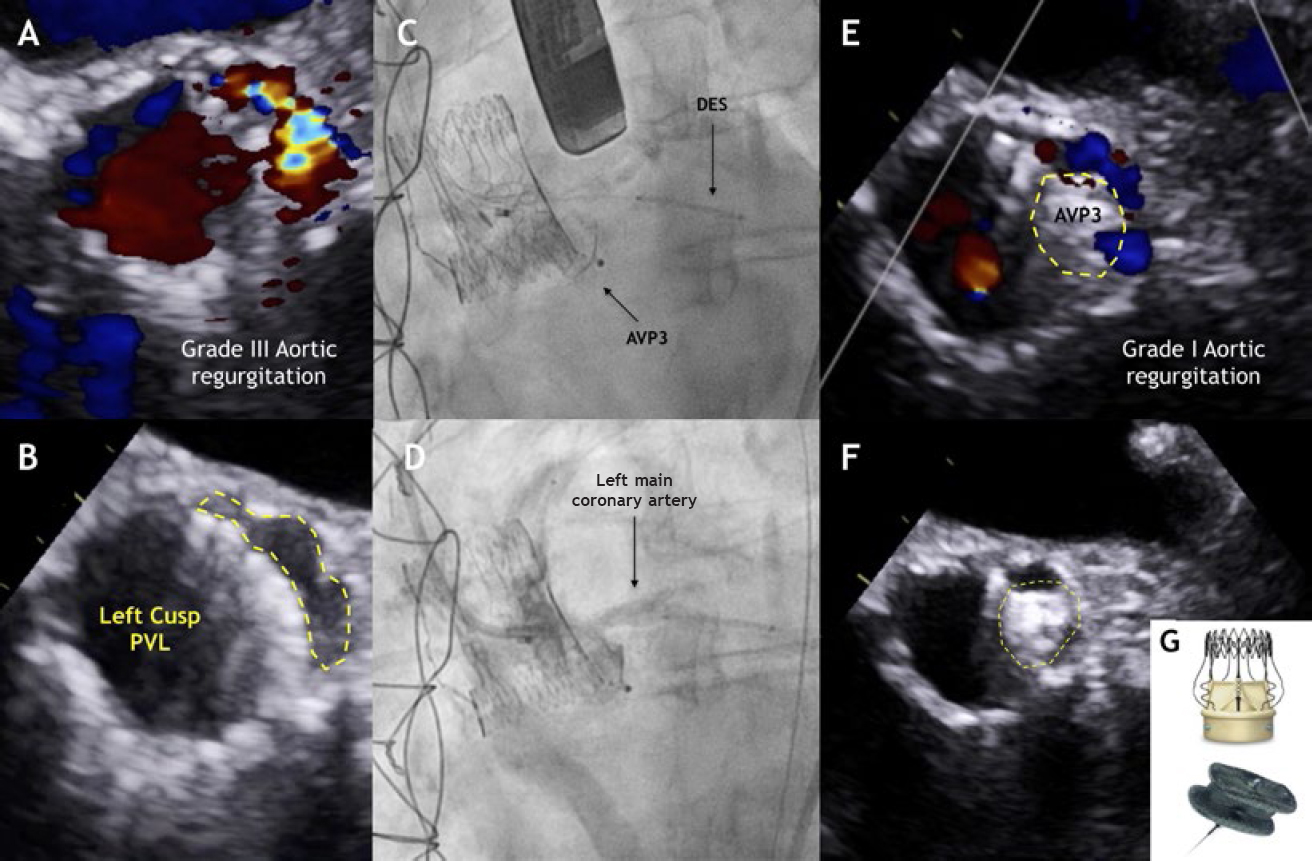
Figure 1.
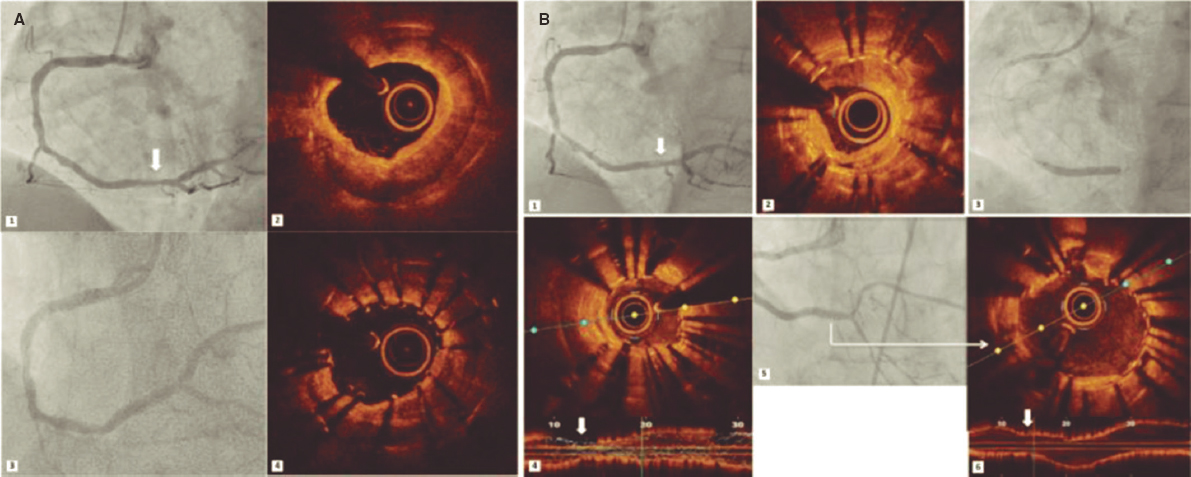
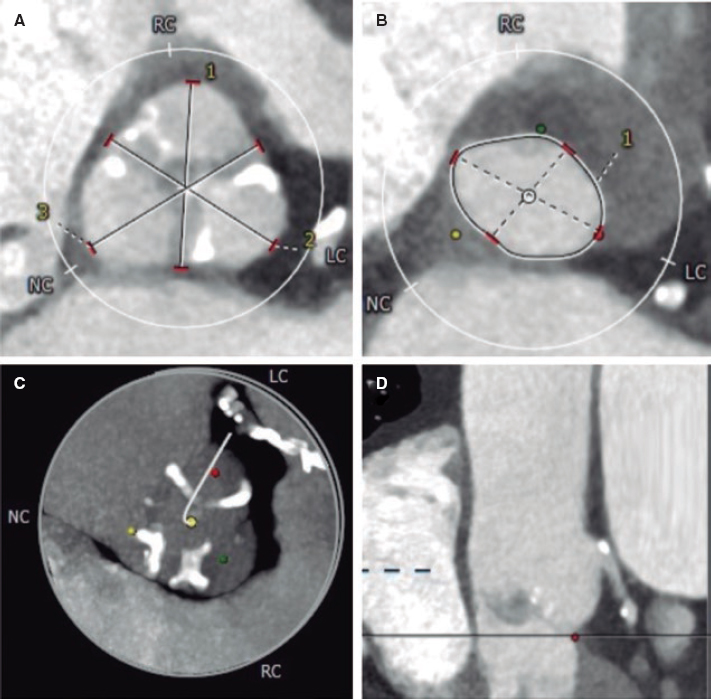
The procedure was performed using a 10x5 mm Amplatzer Vascular Plug III (AVP3) (St. Jude Medical, Plymouth, Minessota, United States) (figure 1C,G, video 3 and video 4 of the supplementary data). An undeployed drug-eluting stent (DES) was positioned in the left main coronary artery (LMCA) to prevent any potential occlusions. After the release, the LMCA remained patent therefore the stent was retrieved (figure 1D, video 5 of the supplementary data). The postprocedural TEE showed significant reduction of the PVL (figure 1E,F). The multi-slice computed tomography (MSCT) was performed at 6 months confirmed the anatomical relationship among the AVP3 device, the Perceval leaflets and the LMCA. Based on the MSCT a 3D model was created that clarified the absence of interference with the valve leaflets or LMCA. The TEE confirmed the presence of a patent LMCA and mild PVL (figure 2, videos 6-8 of the supplementary data).
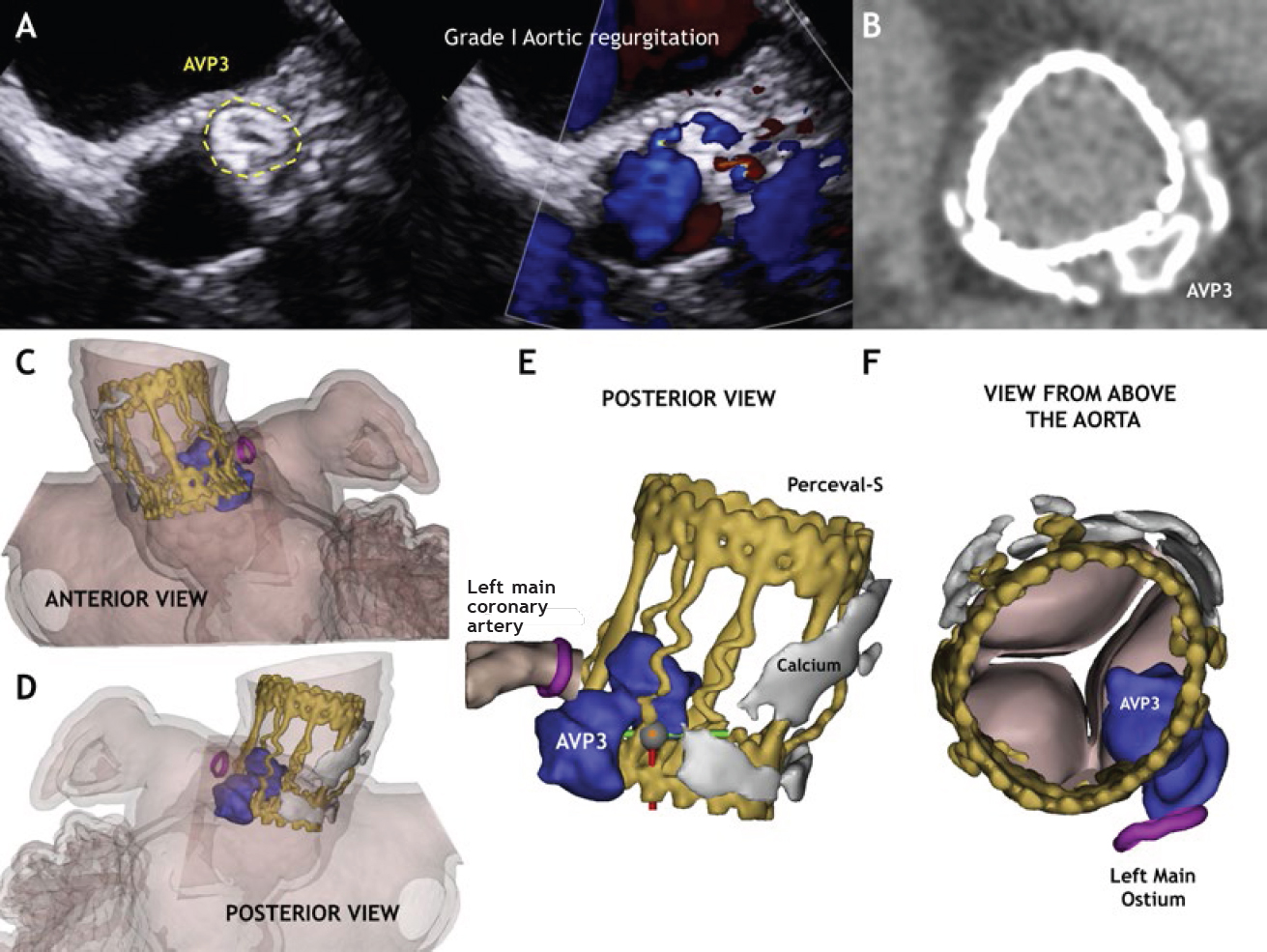
Figure 2.
This is the first case of percutaneous closure of PVL involving a Perceval valve. If the PVL is adjacent to a coronary ostium, protection with an undeployed stent should be considered to prevent an abrupt vessel closure. Three-dimensional models are useful when dealing with complex anatomies for a better understanding of the interaction between the device and surrounding structures.
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Video 1. Rodríguez-Costoya I. DOI:10.24875/RECICE.M19000069
Video 2. Rodríguez-Costoya I. DOI:10.24875/RECICE.M19000069
Video 3. Rodríguez-Costoya I. DOI:10.24875/RECICE.M19000069
Video 4. Rodríguez-Costoya I. DOI:10.24875/RECICE.M19000069
Video 5. Rodríguez-Costoya I. DOI:10.24875/RECICE.M19000069
Video 6. Rodríguez-Costoya I. DOI:10.24875/RECICE.M19000069
Video 7. Rodríguez-Costoya I. DOI:10.24875/RECICE.M19000069
Video 8. Rodríguez-Costoya I. DOI:10.24875/RECICE.M19000069
REFERENCES
1. Her AY, Shin ES. Current Management of In-Stent Restenosis. Korean Circ J. 2018;48:337-349.
2. Alfonso F, Byrne RA, Rivero F, Kastrati A. Current treatment of in-stent restenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:2659-2673.
3. Alfonso F, Rivero F. Network meta-analyses on in-stent restenosis treatment:dealing with complexity to clarify efficacy and safety. J Thorac Dis. 2015;7:1678-1683.
4. Diego A, Pérez de Prado A, Cuellas C, et al. Instent restenosis related to vessel injury score degree. Are current experimental models valid for drug-eluting stents analysis?Rev Esp Cardiol. 2011;64:745-751.
5. Goel SS, Dilip Gajulapalli R, Athappan G, et al. Management of drug eluting stent in-stent restenosis:a systematic review and meta-analysis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;87:1080-1091.
Corresponding author: Department of Interventional Cardiology, Hospital del Mar, Passeig Marítim 25-29, 08003 Barcelona, Spain.
E-mail address: beavaquerizo@yahoo.es (B. Vaquerizo Montilla).